YES
NO
Digital Communications
Division
A development sprint is a 2–3 week cycle that delivers completed functionality at the end.
Development Sprint
Clients
Contractors
If a project is deemed too small to need work by the continuous improvement team, the product owner will create a ticket request in Jira. If the business case does not present a solid justification, the product owner will work to improve things like goals, measures of impact and/or resource estimates.
Create Ticket or
Improve Justification
One or more development sprints may be required to create an MVP. Once the team believes the released functionality meets the minimum viable requirements, it will be sent for MVP assessment.
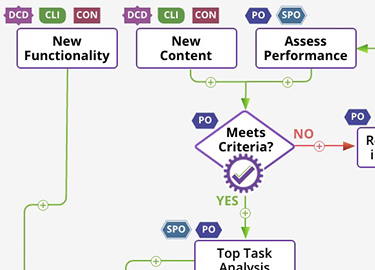
Published website performance will be assessed every 6–12 months to ensure it is on target to meet performance goals established by the product owner and client. Potential adjustments will be identified and/or performance goals shifted as content matures and audience needs evolved.
The design sprint will establish the work to be done by the development team to create a new website.
Assess Performance
Continuous Improvement Scrum Master. The Continuous Improvement Scrum Master is responsible for guiding the work of the continuous improvement development team.
The Scrum Master assists the product development team in meeting their delivery goals.
The SM leads the team and ensures they abide by established Agile practices.
The Senior Product Owner is responsible for creating the business case and user stories for projects requesting continuous improvement efforts. The SPO works closely with the Continuous Improvement Team to ensure the user stories are well understood and scoped. The SPO ensures proper justification is presented to the Venture Team to enable well informed investment.
The Product Owner is responsible for monitoring specific sites’ performance and identifying potential improvement efforts. They are the primary liaison to the content organization, working directly with OpDivs moving to the project H template.
New functionality is presented for an improvement investigation to determine potential impact. This is the flow for “good ideas” based on the team’s observation of technology trends or cross-client requested changes to the project H template.
A determination whether the website meets the criteria for minimally viable product (MVP) can be made based on client and user feedback.
MVP?
If the sprint did not complete the project, its remaining backlog will be prioritized.
If the project backlog is cleared, the website is returned for reassessment in 6–12 months.
Feedback is provided so that justification can be improved with the next assessment. Alternatively, improvements that are deemed small enough can be ticketed in Jira.
Websites and infrastructure are assessed regularly for potential improvement so we can fix it before it breaks.
If a request does not meet the criteria for deeper investigation into improvements, it is returned for reassessment in 6–12 months.
A new website is new content organized in a web entity that a client has requested or an old website that is to be migrated into the project H template for the DCD team to manage.
New content flows into criteria measurement based on topics requested by customer surveys or search terms.
An existing website is a set of web pages that have been migrated to the project
H template.
Websites bring performance measurement from Google Analytics and dashboards to determine whether they meet the criteria for continuous improvement investment.
If a request does meet the criteria for deeper investigation into improvements, it will flow into top task analysis to determine changes needed to top tasks
New
Functionality
New
Content
Assess
Performance
Meets
Criteria?
A project backlog may take more than one sprint to implement. It is not assumed that all the items in the backlog will be completed in sequential sprints unless the result of the sprint is not released functionality.
More Backlog?
Contractors that have been engaged through DCD to assist in building and maintaining hhs.gov websites.
DCD has established a set of criteria
for website performance. This includes things like age, activity levels, site
health, user satisfaction and engagement. The product owner will assess the performance of the site and determine whether it is meeting its performance goals.
Meets Criteria?
Needs
Improvement?
One of the guiding principles is to provide quick access to tasks that have been identified either by the audience or the client as important. These tasks are identified as top either by frequency or by relevance based on the topics covered by the website. Top tasks may shift over time as newsworthy topics and audience needs change.
Approve
Investment?
The development sprint spans 2–3 weeks of focused effort and results in released functionality. The project might take more development cycles to build a release.
Top Task Analysis
Highest
Priority?
OpDivs who have engaged DCD to build and maintain their organization’s websites in the project H template.
Backlog
Empty?
The digital communications division in ASPA, responsible for this governance process and hhs.gov websites.
MVP?
The information gathered in top task analysis and performance investigation is provided to the continuous improvement team for consideration.
Review Again
in 6 Months
If analysis does not reveal important or significant performance shortfalls, it is returned for reassessment in
6–12 months.
Once a deeper analysis of the website has been completed, the product owner and senior product owner will assess the complete list of desired improvements that need to be done. If not enough information is available to make this determination, the website will be returned for reassessment at a later date.
Design (Sprint 0)
Top Task
Analysis
Create Hypothesis
for Change
If analysis reveals important or significant performance shortfalls, the project continues to build a case starting with a proposed change and its impact.
To determine whether functionality meets the minimum user requirements, user testing is conducted with stakeholders and users. This might include scenario testing, usability testing, 508 testing, etc.
From the proposed change, user stories are built and implementation estimates collected with help from the scrum team.
Needs improvement?
User Test
If a website is meeting its performance goals and the product owner deems it does not need improvement at this time, it will be placed back in performance management to be reassessed after 6–12 months.
Once a complete business case has been created it is presented to the venture team to request investment of resources for implementation.
Review Again in 6 Months
The design sprint includes audience interviews, development of the information architecture and creation of user stories that include resource estimates.
Create User Story &
Resource Estimate
The venture team uses a strategic framework and the data presented to decide whether to invest in the proposed improvement.
Present Business
Case to Venture Team
If a project is not approved for investment, it is returned for reassessment after 6–12 months.
If project is approved for investment,
it is added to the queue awaiting resource allocation.
Add Sprint to Continuous
Improvement Queue
Sprints are pulled from the performance queue based on prioritization and availability of resources.
A project that is not the highest priority will wait in the queue for resource allocation until it is the highest priority.
Development
Sprint
A project that is the highest priority will flow to the development team for the next sprint.
Once the sprint is completed, functionality is released. If the sprint did not yield released functionality, the project will receive the highest priority for the next sprint cycle.
After information has been gathered to understand both the cost and the benefit of the requested project, the venture team will make the decision whether to approve the resource investment.
EXISTING WEBSITE
NEW WEBSITE
After a website current state has been assessed, a desired set of changes are identified. The hypothesis for change provides the reason behind the requested changes by identifying the impact that is expected from the change. The hypothesis states, “if we make this change, we will see these results”.
Create Hypothesis for Change
Approve Investment?
ROLES
Agile user stories are created and refined with the help of the continuous improvement team to clearly articulate the new functionality from the user’s perspective. From these user stories, create a resource estimate that provides information on how much effort will be required to implement each user story.
Create User Story &
Resource Estimate
New functionality might be new web site features or infrastructure, or back-end operational components. A client, DCD or contractor team member will propose new functionality based on audience need or technology shifts.
Each sprint on the continuous improvement queue will be prioritized based on impact. The CISM will determine which project to assign to the development team next.
Highest Priority?
New Functionality
Product Owner
The product owner will create a business case that includes a justification based on their hypothesis for change and a resource request based on the estimate provided by the team.
Senior Product Owner
Present Business Case
to Venture Team
Scrum Master
Continuous Improvement
Scrum Master
If MVP assessment deems the release is minimally viable and no further work is required, it will be queued for reassessment in 6–12 months.
Venture Team
If MVP assessment deems the release requires further work, the project is sent into the next sprint cycle.
Development sprints may be followed by user testing to ensure functionality delivers the user stories.
The project will be divided into sprint-sized pieces of work that will at the end, deliver functionality to be tested and refined. A project can be divided into multiple sprints and/or delivered functionality may require more than one sprint to complete. The CISM and SPO manage the continuous improvement queue based on prioritization established with the venture team.
The results from user testing can help to determine whether a site meets the requirements for minimally viable product.
Add Sprint to Continuous Improvement Queue
The Venture Team is responsible for managing DCD resource investment in projects. They are the decision making body in the governance process.
New content is proposed by a client and vetted by the product owner. It represents new pages or sections of the website, and might require information architecture or design changes.
New Content